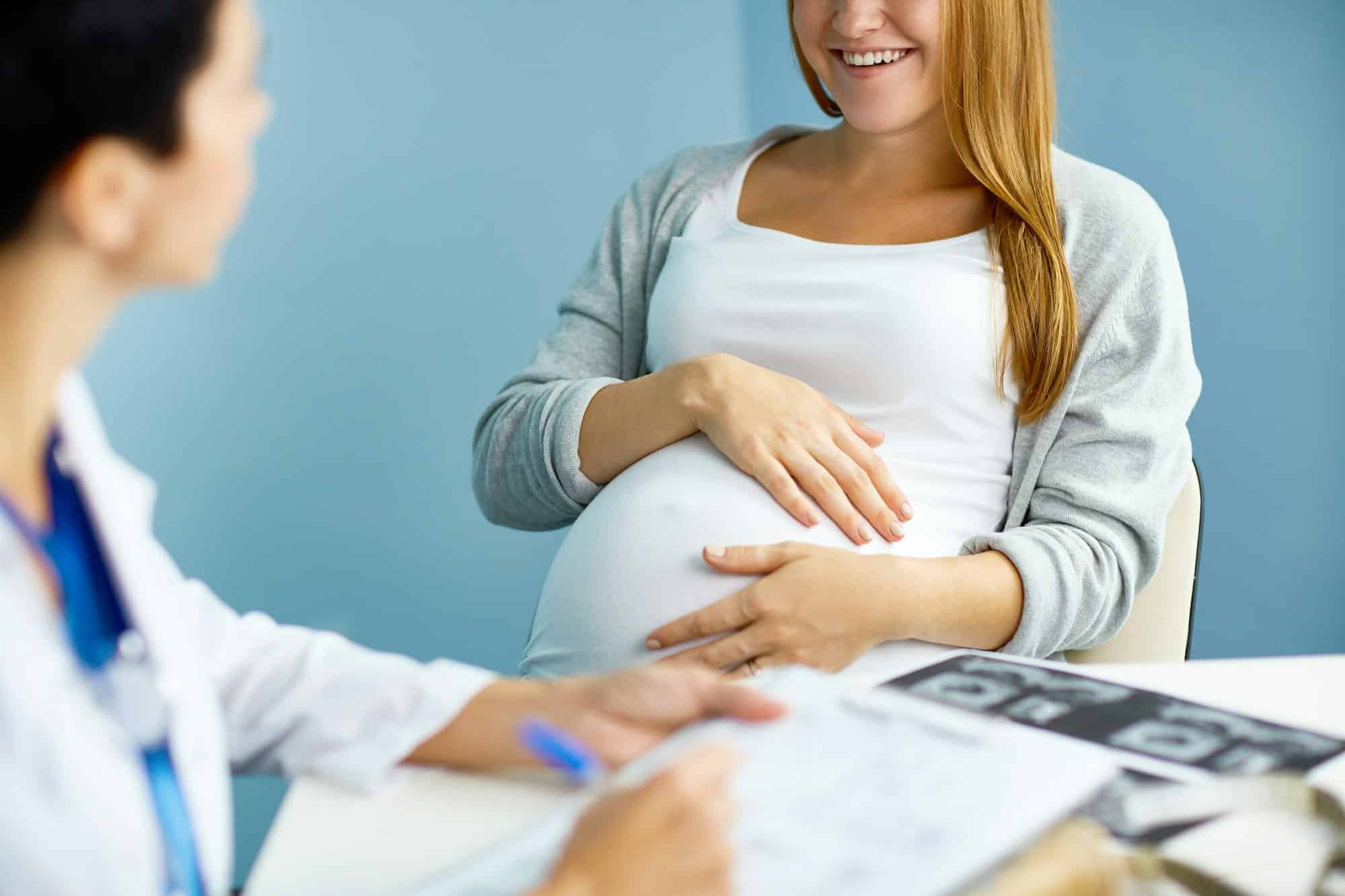
In the ever-evolving field of medical science, the study and understanding of genetics have become increasingly important. Geneticists play a critical role in the identification and treatment of diseases and conditions, particularly those of a hereditary nature. Among these professionals in the United Kingdom, an essential task is the offering of prenatal screening for rare genetic disorders. These screenings offer the potential to identify such conditions in unborn children, helping parents understand the health of their unborn child and make informed decisions.
The Importance of Genetic Screening
The first term to clarify is ‘genetic screening‘. A genetic screening test is a method of identifying gene mutations that could lead to a genetic disorder. It is an essential tool in modern healthcare, and it’s increasingly becoming a standard procedure for pregnant women in many countries, including the UK.
Also read : What new protocols are UK paramedics using to manage acute heart attack symptoms before hospital arrival?
According to PubMed, a free search engine accessing primarily the MEDLINE database of references and abstracts on life sciences and biomedical topics, genetic screening during pregnancy can detect potential health issues that could affect the mother or the unborn child. This information allows healthcare professionals and families to plan for future health needs and, where possible, intervene to improve health outcomes.
The National Health Service (NHS) of the UK, a reliable source of health-related information, emphasizes that genetic screening can help detect a variety of conditions, from common disorders, like Down Syndrome, to rare genetic conditions that could lead to severe health issues or developmental delays.
In the same genre : How can UK urologists use telemedicine to improve follow-up care for prostate cancer patients?
The Role of Geneticists in Prenatal Screening
Geneticists are at the forefront of prenatal screening in the UK. These professionals work closely with families and healthcare providers to offer testing and interpret results. Their role involves conducting laboratory tests to analyze genetic data from samples of body fluids and tissues.
One of the popular tools used by geneticists for their research is Google Scholar, a freely accessible web search engine that indexes the full text or metadata of scholarly literature across an array of publishing formats and disciplines. Through this platform, geneticists can access the latest research, advancements, and findings in the field of genetics to reinforce their practice and provide the most up-to-date care.
As part of the screening process, geneticists will conduct a thorough family health history. This process involves asking questions about the health of relatives to identify if any genetic disorders may run in the family.
An Overview of Testing Procedures
When you undergo genetic testing, it typically involves taking a sample of your blood, hair, skin, or other tissue and examining it in a laboratory. The aim is to detect specific changes in chromosomes, genes, or proteins that could indicate a genetic disorder.
They may recommend certain tests based on the family health history or if the pregnant woman is at an increased risk due to her age or other factors. Once the tests are conducted, geneticists will then interpret the results, offering insights into the potential risks and conditions that the unborn child may inherit.
The Potential Impact of Genetic Screening
Genetic screening, particularly prenatal screening, can have a profound impact on families. It can provide early detection of a condition, which can lead to early intervention and potentially better health outcomes. For some families, it may influence decisions about having children or preparing for a child with special needs.
However, it’s crucial to remember that genetic screening does not provide certainty. A positive screening result does not definitely mean the child will develop the condition. It merely indicates a higher risk. Geneticists play a crucial role in helping parents understand these nuances, providing the necessary support and guidance during this potentially stressful period.
Ethics and Considerations in Genetic Screening
Finally, it’s important to point out the ethical considerations that come with genetic screening. Geneticists, along with the entire healthcare team, must ensure that families fully understand the tests, their purpose, and potential outcomes. They must also respect the family’s decisions regarding testing and the choices they make based on the test results.
Geneticists are obligated to handle these situations with sensitivity and professionalism, guiding families through the process while respecting their rights and autonomy.
As genetic technologies continue to advance, the role of geneticists in prenatal screening will likely become more prominent. They stand at the forefront of this exciting field, guiding families through complex decisions and helping to pave the way for healthier futures.
Advanced Genetic Tools and the Role of Geneticists
In the current era of advanced genetics, tools such as Google Scholar and PubMed have become indispensable for geneticists. They provide free access to a wide range of scholarly articles, research findings and clinical trials in the field of genetics. These databases are regularly updated with new discoveries and developments, aiding geneticists in staying abreast with the latest trends and techniques in their field.
Geneticists in the UK don’t just rely on existing data, but they also contribute to these databases with their extensive research in the field of prenatal screening. A key aspect of their job is to offer genetic testing for pregnant women to screen for rare genetic conditions in the unborn child.
Geneticists conduct these tests by collecting samples of blood, hair, skin or other tissues from the pregnant woman. They then examine these samples in a laboratory, aiming to detect specific changes in chromosomes, genes, or proteins that could indicate a genetic disorder.
They may also conduct a thorough family health history to understand if there is a predisposition to any genetic conditions. This involves asking detailed questions about the health history of close relatives, looking for patterns or clues that may suggest a genetic disorder.
Post testing, geneticists interpret the results and communicate their findings to the family. They provide insights into the potential risks and conditions that the unborn child may inherit. This information can be crucial in helping parents make informed decisions about the pregnancy and preparation for the care of the child.
Conclusion: The Future of Genetic Screening in the UK
Indeed, the work of geneticists in the field of prenatal screening for rare genetic disorders in the UK is invaluable. Their efforts have a profound impact on public health, shaping the future of families and individuals who are at risk of inheriting such conditions.
Their role doesn’t end with the delivery of test results. Geneticists are required to guide families through the interpretive process, helping them understand the implications of the results and offering them the necessary support. Likewise, geneticists are tasked with addressing ethical considerations such as ensuring informed consent, respecting the family’s decisions, and maintaining confidentiality.
From the early detection of conditions like cystic fibrosis and breast cancer, to guiding families through complex decisions, geneticists play a pivotal role in healthcare. As genetic technologies continue to evolve and improve, their role is set to become even more crucial.
This will inevitably bring new challenges and ethical considerations that will need to be addressed. Yet, with their expertise and commitment, geneticists in the UK are well-positioned to navigate these complexities, ultimately enhancing the health and wellbeing of the public. Public health can look forward to a future with improved genetic services and a better understanding of rare genetic conditions, paving the way for healthier generations.